Contact us
- Burjuman Business Tower Office 2414 Bur Dubai, P.O. Box: 390667, Dubai UAE
- healthcare@gazminintl.com
- (+971) 4235 5866 / 67
-
Monday – Friday :
9:00 AM – 6:00 PM
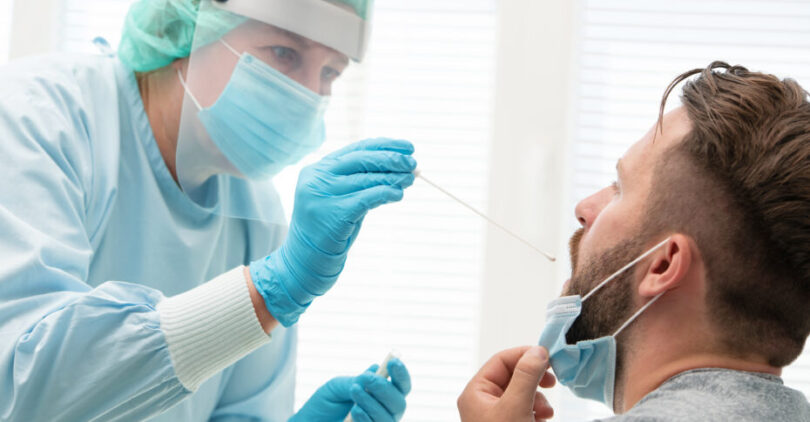
Types of tests for detecting COVID-19
PCR testing
- Swab testing
It’s the most common type of testing is polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which is considered fairly reliable since PCR tests are 95 % effective and accurate.
An RNA sample (the nucleic acid that transforms DNA into proteins) is collected from the patient’s tonsils and inside their nose for PCR testing using a swab. This test collects RNA since it contains the genetic information of this particular virus.
The sample is then transferred to a laboratory, where it is heated and cooled in order to multiply into larger quantities of DNA. Bio scientists may then determine the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus (the virus that causes COVID-19)
PCR test results take around two days because the process takes place in a laboratory.
- RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction) test
In many countries, the RT-PCR test is considered a standard test for diagnosing COVID-19. A nasal swab is used to obtain the sample for the screening. This technique detects SARS-CoV-2 genetic material or RNA from a person’s upper and lower respiratory specimens in real time.
- 90-minute PCR test
Machines that can perform on-the-spot genetic testing have been introduced, and RNA is being collected for PCR testing, which can also detect the common flu.
The RNA is extracted from swab samples and placed into a cartridge, which is then inserted into a machine that performs a PCR test and determines whether the virus is present within 90 minutes.
Antigen testing
These tests detect for antigens, which are proteins found on the surface of viruses. Antigens may be easily detected in saliva, and laboratory testing is not required, thus it can be done in locations such as nursing homes and without the assistance of a medical expert.
With several systems now available and many more being developed, results may be delivered faster than PCR testing, and infections can be identified within 20 minutes.
Antibody testing (also known as serology tests)
Antibody or serology tests, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention- CDC, look for antibodies in a person’s blood to identify if he has previously been infected with the virus that causes COVID-19. Antibody testing offer valuable information for treating COVID-19, analyzing its spread, and determining potential implications for human resource planning.
Laser-based DPI technology (Diffractive Phase Interferometry)
Laser technology is utilized in this sort of test to analyse blood samples in order to detect the virus. It enables health officials to do large-scale screening in a matter of seconds to discover suspected cases of infection before they undertake Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) swab tests. It is used as a preliminary step in detecting suspected cases of infection before they are subjected to a PCR test. It is easy to use as it is non-invasive, and inexpensive.
LAMP testing
LAMP (Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification) is a technique similar to PCR testing, but instead of heating and cooling, it creates much more viral RNA copies at a constant temperature, allowing for a considerably faster result – within a couple of hours or even less.
Samples from the nose and throat are taken with a swab, or mucus from severe coughing can also be used. The swabbing does not have to be as thorough as the PCR test.
The samples are then put in vials of reagents (substances that cause a chemical reaction to detect RNA) and heated for 20 minutes in a specific machine.
The machine next analyzes the sample to see if any SARS-CoV-2 RNA is present.
- The RT-LAMP test (Reverse Transcription LAMP)
When compared to the PCR test, this test provides for a faster analysis. It is carried out by collecting a nasal swab and exposing it to equal-tempered circumstances. Within an hour, results are generated.
- No-swab saliva test
The ease of this test is that patients can perform it at home by collecting around two millimeters of saliva into a sample pot and sending it to a laboratory. In many countries, if collecting a nose swab is not possible, the saliva test is used to detect infection in children aged 3 to 16 years.
The sample is analyzed in a lab utilizing LAMP technology, and the results are texted to the patient.
It still takes around 48 hours, but the advantage of this test is that the patient does not have to leave their house or stick a swab down their throat or up their nose.
